Login
 USD $
USD $
 AUD AUD
AUD AUD CAD CAD
CAD CAD GBP £
GBP £ EUR €
EUR €
All Categories
(0) My Cart (0)
LambskinMushroom DildoNew ArrivalCheap
pleated filter cartridge factory
high flow filter cartridge
large flow filter cartridge
membrane pleated filter cartridge
capsule filter suppliers
capsule filter 0.2 micron
capsule filter price
capsule filter
water filter cartridge
New Products
The top ten AIDS prevention issues that netizens are most concerned about on AIDS Day
1. How does AIDS spread?
A: HIV spreads through the following three ways.
Sexual transmission, blood transmission and mother-to-child transmission.
2. Is it dangerous to work with people living with HIV?
A: contact with HIV-infected people and patients in their daily life and work will not be infected with AIDS.
(1) General contact with HIV-infected people and patients in work and life, such as handshakes, hugs, courtesy kisses, shared meals and sharing labor tools, office appliances, coins, etc., will not be infected with HIV.
(2) HIV does not spread through public facilities such as toilet seats, telephones, tableware, bedding, swimming pools or public baths.
(3) coughing and sneezing do not spread HIV.
(4) mosquito bites do not transmit HIV.
3. Which behaviors are easy to be infected with AIDS?
Answer: we usually call the behaviors that are easy to cause HIV infection as high-risk behaviors as follows: 1. The high-risk behaviors through sexual channels are: unprotected sexual intercourse, multiple sexual partners women vibrator , and so on. 2. High-risk behaviors through blood pathway include intravenous drug abuse, sharing syringes or other instruments that can pierce the skin with others, and using untested blood or blood products. 3. The high-risk behaviors through mother-to-child route are: HIV-positive women become pregnant and give birth, and HIV-positive mothers breastfeed, all of which may cause HIV infection in their children. 4. other ways that can cause blood transmission, such as: knives used for hairdressing, cosmetology, tattoos, ear piercing, pedicure, etc.; sharing razors, electric razors and toothbrushes with others; bleeding caused by sports injuries and fights; when rescuing the wounded, the broken skin of the rescuer touches the blood of the injured.
4. How to know that a person is infected with AIDS?
Answer: to determine whether a person is infected with HIV, the usual test method is to go to local health institutions to test for HIV antibodies in the blood. If the antibody test is positive, it shows that the person has been infected with HIV.
However, after the human body is infected with HIV, it usually takes 2 weeks to gradually produce antibodies to the virus. The period from HIV infection to the detection of antibodies to the virus in peripheral blood is called the "window period", usually 2 weeks-3 months. During this period, no viral antibodies were detected in the blood, but they were contagious.
5, the occurrence of high-risk behavior, and infected with sexually transmitted diseases, is it possible to be infected with AIDS?
Answer: AIDS also belongs to a kind of venereal disease, its route of transmission, risk behavior anal dildo , involving people and preventive measures have a lot in common with general venereal diseases. A venereal disease patient can be infected with a variety of venereal diseases at the same time. For example, syphilis patients can be infected with gonorrhea or AIDS at the same time. And STD patients often suffer from ulcers in the vulva and external genitalia, providing favorable conditions for the invasion of HIV, making it easy to enter the human body and spread rapidly. At the same time, STD pathogens infect people, often cause local inflammation, and inflammation makes lymphocytes increase, because lymphocytes are the target cells of HIV attack, so its rapid increase has played a role in attracting HIV invasion.
6. Will you die soon after you are infected with AIDS?
A: from the time HIV entered the human body, the human body began to fight against it. It takes time for the virus to reproduce in the human body. In the initial stage, the immune function of infected people has not been seriously damaged, so there are no obvious symptoms ed vacuum pump , we call such people infected with HIV. When the immune function of the infected person is destroyed to a certain extent, other germs will swoop in and cause a variety of diseases, which are generally called opportunistic infections, such as severe diarrhea, pneumonia or some cancers. At this time, the infected person becomes an AIDS patient. From HIV-infected people to AIDS patients can be developed from a few months to several years, usually 2-10 years. As long as they do not enter the onset period, people living with HIV can live and work like normal people. Moreover, the current antiviral treatment can effectively prolong the lives of patients, so people infected with HIV, do not give up, but to find ways to delay the disease.
7. How to prevent AIDS?
A: AIDS is a behavioral disease. The following preventive measures can be taken against the three routes of transmission of AIDS.
Prevention of transmission through sexual contact: abiding by sexual morality, fixed sexual partners, and safe sex are effective measures to prevent the sexual transmission of AIDS. The correct use of qualified condoms (condoms) can reduce the risk of HIV infection. If you have sexually transmitted diseases or suspected venereal diseases, you should go to designated medical institutions or regular hospitals for examination and treatment as soon as possible.
Prevention of blood transmission: stay away from drugs and resist drugs; for those who are unfortunately addicted to drugs, they should be helped to quit; for those who are temporarily unable to quit, methadone replacement therapy (also known as maintenance treatment) and clean needle exchange can be used to change the behavior of sharing syringes and block the spread of HIV. Do not accept blood, blood products and organs that have not been tested for HIV antibodies; do not use syringes that have not been strictly sterilized; do not share syringes and razors with others; and vigorously promote the use of disposable syringes and other safe injection measures.
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission: women infected with HIV should avoid pregnancy; once pregnant, consider whether to terminate the pregnancy under the guidance of a doctor; those who choose to continue pregnancy should take measures such as antiviral intervention and cesarean section to block transmission, and avoid breastfeeding newborns after delivery.
8. What are the national policies for HIV-infected people and patients?
A: at present, our government has implemented the policy of "four exemptions and one care" in the prevention and treatment of AIDS. The "four exemptions" refer to the provision of antiviral drugs free of charge to AIDS patients in rural residents and urban people with financial difficulties who do not participate in the basic medical insurance system; provide free counseling and primary screening and testing for people who voluntarily undergo AIDS counseling and testing nationwide; provide free maternal and infant blocking drugs and infant testing reagents for pregnant women infected with HIV; and waive school fees for orphans of AIDS patients. "one care" refers to bringing AIDS patients with living difficulties into the scope of government assistance and giving them necessary life relief in accordance with the relevant provisions of the state. Actively support productive AIDS patients. Avoid discrimination against people living with HIV / AIDS and patients.
9. Will personal information be released when HIV infection and AIDS patients are detected?
A: the personal information of people living with HIV and AIDS will be protected by the relevant departments. Article 39 of the regulations on the Prevention and Control of AIDS stipulates that without the consent of himself or his guardian, no unit or individual may disclose the names, addresses, work units, portraits, medical history materials and other information that may infer their specific identities of people infected with HIV, AIDS patients and their families.
10. Who are easily infected with AIDS?
Answer: mainly include the following categories: gay men, prostitutes and prostitutes, multiple sexual partners, STD patients, injecting drug users and babies whose parents suffer from AIDS.
Realistic dildo | best vibrator | pvc dildo | fat pocket pussy
A: HIV spreads through the following three ways.
Sexual transmission, blood transmission and mother-to-child transmission.
2. Is it dangerous to work with people living with HIV?
A: contact with HIV-infected people and patients in their daily life and work will not be infected with AIDS.
(1) General contact with HIV-infected people and patients in work and life, such as handshakes, hugs, courtesy kisses, shared meals and sharing labor tools, office appliances, coins, etc., will not be infected with HIV.
(2) HIV does not spread through public facilities such as toilet seats, telephones, tableware, bedding, swimming pools or public baths.
(3) coughing and sneezing do not spread HIV.
(4) mosquito bites do not transmit HIV.
3. Which behaviors are easy to be infected with AIDS?
Answer: we usually call the behaviors that are easy to cause HIV infection as high-risk behaviors as follows: 1. The high-risk behaviors through sexual channels are: unprotected sexual intercourse, multiple sexual partners women vibrator , and so on. 2. High-risk behaviors through blood pathway include intravenous drug abuse, sharing syringes or other instruments that can pierce the skin with others, and using untested blood or blood products. 3. The high-risk behaviors through mother-to-child route are: HIV-positive women become pregnant and give birth, and HIV-positive mothers breastfeed, all of which may cause HIV infection in their children. 4. other ways that can cause blood transmission, such as: knives used for hairdressing, cosmetology, tattoos, ear piercing, pedicure, etc.; sharing razors, electric razors and toothbrushes with others; bleeding caused by sports injuries and fights; when rescuing the wounded, the broken skin of the rescuer touches the blood of the injured.
4. How to know that a person is infected with AIDS?
Answer: to determine whether a person is infected with HIV, the usual test method is to go to local health institutions to test for HIV antibodies in the blood. If the antibody test is positive, it shows that the person has been infected with HIV.
However, after the human body is infected with HIV, it usually takes 2 weeks to gradually produce antibodies to the virus. The period from HIV infection to the detection of antibodies to the virus in peripheral blood is called the "window period", usually 2 weeks-3 months. During this period, no viral antibodies were detected in the blood, but they were contagious.
5, the occurrence of high-risk behavior, and infected with sexually transmitted diseases, is it possible to be infected with AIDS?
Answer: AIDS also belongs to a kind of venereal disease, its route of transmission, risk behavior anal dildo , involving people and preventive measures have a lot in common with general venereal diseases. A venereal disease patient can be infected with a variety of venereal diseases at the same time. For example, syphilis patients can be infected with gonorrhea or AIDS at the same time. And STD patients often suffer from ulcers in the vulva and external genitalia, providing favorable conditions for the invasion of HIV, making it easy to enter the human body and spread rapidly. At the same time, STD pathogens infect people, often cause local inflammation, and inflammation makes lymphocytes increase, because lymphocytes are the target cells of HIV attack, so its rapid increase has played a role in attracting HIV invasion.
6. Will you die soon after you are infected with AIDS?
A: from the time HIV entered the human body, the human body began to fight against it. It takes time for the virus to reproduce in the human body. In the initial stage, the immune function of infected people has not been seriously damaged, so there are no obvious symptoms ed vacuum pump , we call such people infected with HIV. When the immune function of the infected person is destroyed to a certain extent, other germs will swoop in and cause a variety of diseases, which are generally called opportunistic infections, such as severe diarrhea, pneumonia or some cancers. At this time, the infected person becomes an AIDS patient. From HIV-infected people to AIDS patients can be developed from a few months to several years, usually 2-10 years. As long as they do not enter the onset period, people living with HIV can live and work like normal people. Moreover, the current antiviral treatment can effectively prolong the lives of patients, so people infected with HIV, do not give up, but to find ways to delay the disease.
7. How to prevent AIDS?
A: AIDS is a behavioral disease. The following preventive measures can be taken against the three routes of transmission of AIDS.
Prevention of transmission through sexual contact: abiding by sexual morality, fixed sexual partners, and safe sex are effective measures to prevent the sexual transmission of AIDS. The correct use of qualified condoms (condoms) can reduce the risk of HIV infection. If you have sexually transmitted diseases or suspected venereal diseases, you should go to designated medical institutions or regular hospitals for examination and treatment as soon as possible.
Prevention of blood transmission: stay away from drugs and resist drugs; for those who are unfortunately addicted to drugs, they should be helped to quit; for those who are temporarily unable to quit, methadone replacement therapy (also known as maintenance treatment) and clean needle exchange can be used to change the behavior of sharing syringes and block the spread of HIV. Do not accept blood, blood products and organs that have not been tested for HIV antibodies; do not use syringes that have not been strictly sterilized; do not share syringes and razors with others; and vigorously promote the use of disposable syringes and other safe injection measures.
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission: women infected with HIV should avoid pregnancy; once pregnant, consider whether to terminate the pregnancy under the guidance of a doctor; those who choose to continue pregnancy should take measures such as antiviral intervention and cesarean section to block transmission, and avoid breastfeeding newborns after delivery.
8. What are the national policies for HIV-infected people and patients?
A: at present, our government has implemented the policy of "four exemptions and one care" in the prevention and treatment of AIDS. The "four exemptions" refer to the provision of antiviral drugs free of charge to AIDS patients in rural residents and urban people with financial difficulties who do not participate in the basic medical insurance system; provide free counseling and primary screening and testing for people who voluntarily undergo AIDS counseling and testing nationwide; provide free maternal and infant blocking drugs and infant testing reagents for pregnant women infected with HIV; and waive school fees for orphans of AIDS patients. "one care" refers to bringing AIDS patients with living difficulties into the scope of government assistance and giving them necessary life relief in accordance with the relevant provisions of the state. Actively support productive AIDS patients. Avoid discrimination against people living with HIV / AIDS and patients.
9. Will personal information be released when HIV infection and AIDS patients are detected?
A: the personal information of people living with HIV and AIDS will be protected by the relevant departments. Article 39 of the regulations on the Prevention and Control of AIDS stipulates that without the consent of himself or his guardian, no unit or individual may disclose the names, addresses, work units, portraits, medical history materials and other information that may infer their specific identities of people infected with HIV, AIDS patients and their families.
10. Who are easily infected with AIDS?
Answer: mainly include the following categories: gay men, prostitutes and prostitutes, multiple sexual partners, STD patients, injecting drug users and babies whose parents suffer from AIDS.
Realistic dildo | best vibrator | pvc dildo | fat pocket pussy
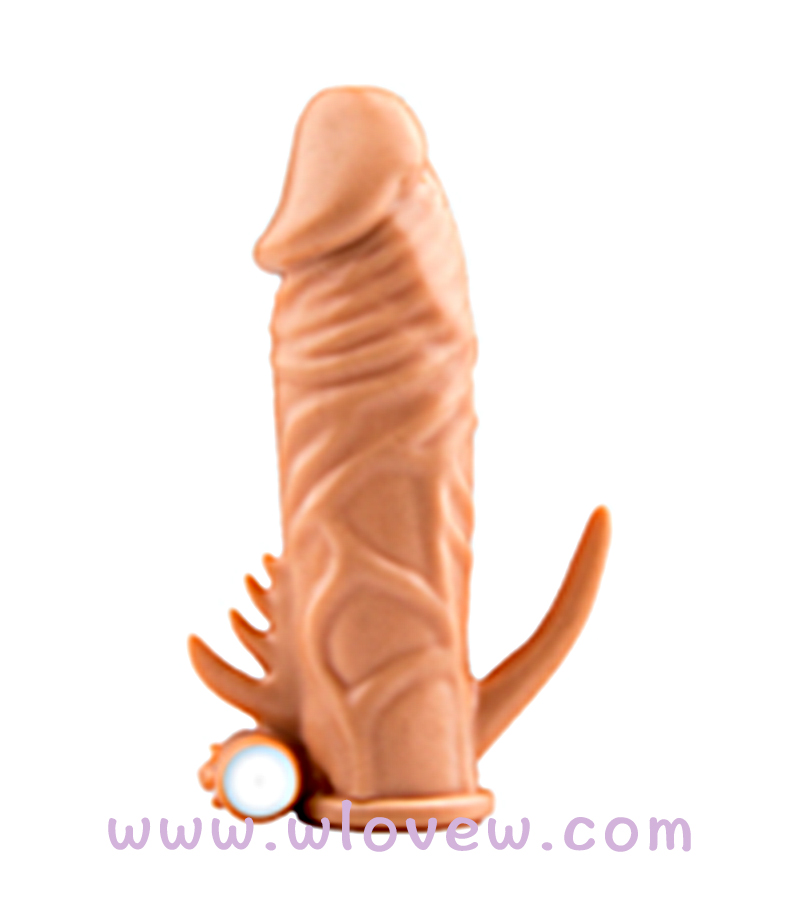

- Dildo cover - Type C
- $7.82
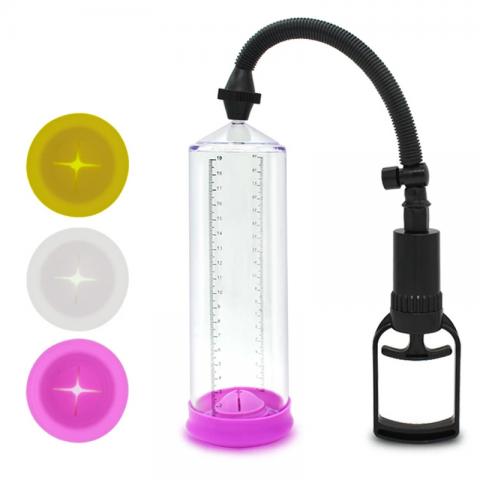

- Premium Penis Pump
- $11.90
Read More huge dildo
Subscribe for Join Us!
Subcribe to get $10 OFF for order.
- Information
- About us
- Contact us
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
- Shopping Guide
- Payment Methods
- Products
- Dildos
- Vibrators
- Penis Pumps
- Masturbation Cup
- Love Egg
- Contact Us
- [email protected]
- Room 1003, Chevalier House, 188 Chatham Road South, Tsim Sha Tsui, Kowloon, Hong Kong
CopyRight © wlovew.com 2002-2025













-
Follow Us On WhatsApp
My Cart (0)
Follow Us On WhatsApp